I started chemistry with a boxed set in 1962. In those days they contained serious amounts of chemicals, but I very soon ran out of most of them. Two discoveries turned what might have been a typical discarded christmas present into a lifelong career and hobby.
Chemistry in the early 1960s: a reminiscence.
December 22nd, 2014Data discoverability
December 17th, 2014I have written earlier about the Amsterdam Manifesto. That arose out of a conference on the theme of “beyond the PDF“, with one simple question at its heart: what can be done to liberate data from containers it was not designed to be in? The latest meeting on this topic will happen in January 2015 as FORCE2015.
Halogen bonds 4: The strongest (?) halogen bond.
December 7th, 2014
Continuing my hunt, here is a candidate for a strong(est?) halogen bond, this time between Se and I.[1]. 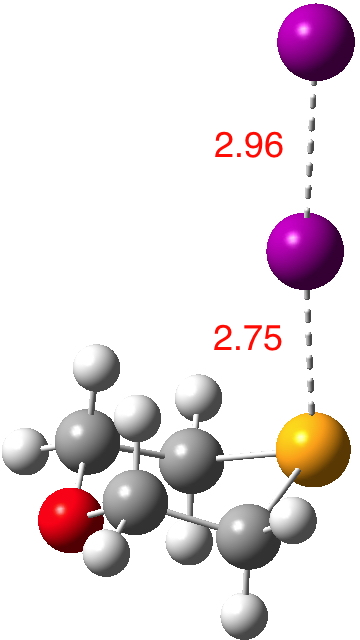 The features of interest include:
The features of interest include:
References
- H. Maddox, and J.D. McCullough, "The Crystal and Molecular Structure of the Iodine Complex of 1-Oxa-4-selenacyclohexane, C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>8</sub>OSe.I<sub>2</sub>", Inorganic Chemistry, vol. 5, pp. 522-526, 1966. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic50038a006
Halogen bonds 3: “Nitrogen tri-iodide”
December 1st, 2014Nitrogen tri-iodide, or more accurately the complex between it and ammonia ranks amongst the oldest known molecules (1812). I became familiar with it around the age of 12-13, in an era long gone when boys (and very possibly girls too) were allowed to make such substances in their parent’s back gardens‡ and in fact in the school science laboratory,† an experiment which earned me a personal request to visit the head teacher.
Halogen bonds 2: The DABCO-Iodine structure.
November 30th, 2014Pursuing the topic of halogen bonds, the system DABCO (a tertiary dibase) and iodine form an intriguing complex. Here I explore some unusual features of the structure HEKZOO[1] as published in 2012[2] and ask whether the bonding between the donor (N) and the acceptor (I-I) really is best described as a “non-covalent-interaction” (NCI) or not.
References
- Peuronen, A.., Valkonen, A.., Kortelainen, M.., Rissanen, K.., and Lahtinen, M.., "CCDC 879935: Experimental Crystal Structure Determination", 2013. https://doi.org/10.5517/ccyjn03
- A. Peuronen, A. Valkonen, M. Kortelainen, K. Rissanen, and M. Lahtinen, "Halogen Bonding-Based “Catch and Release”: Reversible Solid-State Entrapment of Elemental Iodine with Monoalkylated DABCO Salts", Crystal Growth & Design, vol. 12, pp. 4157-4169, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg300669t
The solvation of ion pairs.
November 6th, 2014Solvolytic mechanisms are amongst the oldest studied, but reproducing their characteristics using computational methods has been a challenging business. This post was inspired by reading Steve Bachrach’s post, itself alluding to this aspect in the title “Computationally handling ion pairs”. It references this recent article on the topic[1] in which the point is made that reproducing the features of both contact and solvent-separated ion pairs needs a model comprising discrete solvent molecules (in this case four dichloromethane units) along with a continuum model.
References
- T. Hosoya, T. Takano, P. Kosma, and T. Rosenau, "Theoretical Foundation for the Presence of Oxacarbenium Ions in Chemical Glycoside Synthesis", The Journal of Organic Chemistry, vol. 79, pp. 7889-7894, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo501012s
Blasts from the past. A personal Web presence: 1993-1996.
November 1st, 2014Egon Willighagen recently gave a presentation at the RSC entitled “The Web – what is the issue” where he laments how little uptake of web technologies as a “channel for communication of scientific knowledge and data” there is in chemistry after twenty years or more. It caused me to ponder what we were doing with the web twenty years ago. Our HTTP server started in August 1993, and to my knowledge very little content there has been deleted (it’s mostly now just hidden). So here are some ancient pages which whilst certainly not examples of how it should be done nowadays, give an interesting historical perspective. In truth, there is not much stuff that is older out there!
Halogen bonds: Part 1.
November 29th, 2014Halogen bonds are less familiar cousins to hydrogen bonds. They are defined as non-covalent interactions (NCI) between a halogen atom (X, acting as a Lewis acid, in accepting electrons) and a Lewis base D donating electrons; D….X-A vs D…H-A. They are superficially surprising, since both D and X look like electron rich species. In fact the electron distribution around X-X (A=X) is highly anisotropic, with the electron rich distribution (the "donor") being in a torus encircling the bond, and an electron deficient region (the "acceptor") lying along the axis of the bond.
Read the rest of this entry »
Tags: crystal structure search, D. Note, frequent commentator, Paul Schleyer
Posted in crystal_structure_mining, Interesting chemistry, reaction mechanism | No Comments »