February 1st, 2016
I attended the first (of a proposed five) workshops organised by LEARN (an EU-funded project that aims to ...Raise awareness in research data management (RDM) issues & research policy) on Friday. Here I give some quick bullet points relating to things that caught my attention and or interest. The program (and Twitter feed) can be found at https://learnrdm.wordpress.com where other's comments can also be seen.
Read the rest of this entry »
Tags: Academic publishing, European Union, first Open Scientist, first secretary, Free culture movement, Henry Oldenburg, Jean Claude Bradley, Open access, Open data, Open science, RDM, Research, researcher, Royal Society, Science, Scientific method, Scientific misconduct, scientist, Technology/Internet
Posted in Chemical IT | 1 Comment »
January 31st, 2016
Six years ago, I posted on the nature of a then recently reported[cite]10.1002/anie.200803859[/cite] Cr-Cr quintuple bond. The topic resurfaced as part of the discussion on a more recent post on NSF3, and a sub-topic on the nature of the higher order bonding in C2. The comment made a connection between that discussion and the Cr-Cr bond alluded to above. I responded briefly to that comment, but because I want to include 3D rotatable surfaces, I expand the discussion here and not in the comment.‡
Read the rest of this entry »
Tags: Chemical bond, chemical bonding, Electron, Electron configuration, energy, Molecular orbital, Multi-configurational self-consistent field, Quantum chemistry, quintuple bond, search term, Transition metal, Valence bond theory
Posted in General, Interesting chemistry | 6 Comments »
January 20th, 2016
The original strategic objective of my PhD researches in 1972-74 was to explore how primary kinetic hydrogen isotope effects might be influenced by the underlying structures of the transition states involved. Earlier posts dealt with how one can construct quantum-chemical models of these transition states that fit the known properties of the reactions. Now, one can reverse the strategy by computing the expected variation with structure to see if anything interesting might emerge, and then if it does, open up the prospect of further exploration by experiment. Here I will use the base-catalysed enolisation of 1,3-dimethylindolin-2-ones and the decarboxylation of 3-indole carboxylates to explore this aspect.
Read the rest of this entry »
Tags: aqueous solution, Brian Challis, can construct quantum-chemical models, computed free energy barrier matches, Dan Singleton, free energy barrier, free energy barriers, Kinetic isotope effect, Organic chemistry, Physical organic chemistry, quantum-chemical models, supervisor
Posted in reaction mechanism | No Comments »
January 16th, 2016
The post on applying VSEPR ("valence shell electron pair repulsion") theory to the geometry of ClF3 has proved perennially popular. So here is a follow-up on another little molecue, F3SN. As the name implies, it is often represented with an S≡N bond. Here I take a look at the conventional analysis.
Read the rest of this entry »
Tags: Chemical bond, chemical bonding, Electron, Lone pair, Molecular geometry, Octet rule, Quantum chemistry, Stereochemistry, Tetrahedral molecular geometry, Theoretical chemistry, Valence, VSEPR theory
Posted in Hypervalency | 110 Comments »
January 10th, 2016
Earlier I explored models for the heteroaromatic electrophilic protiodecarboxylation of an 3-substituted indole, focusing on the role of water as the proton transfer and delivery agent. Next, came models for both water and the general base catalysed ionization of indolinones. Here I explore general acid catalysis by evaluating the properties of two possible models for decarboxylation of 3-indole carboxylic acid, one involving proton transfer (PT) from neutral water in the presence of covalent un-ionized HCl (1) and one with PT from a protonated water resulting from ionised HCl (2).
Read the rest of this entry »
Tags: Acid, Acids, bicyclic network, carboxylic acid, free energy, Functional groups, Hydrogen bond, Indole, transition state free energy
Posted in Interesting chemistry | 1 Comment »
January 7th, 2016
This is the third and final study deriving from my Ph.D.[cite]10.1039/P29750001822[/cite]. The first two topics dealt with the mechanism of heteroaromatic electrophilic attack using either a diazonium cation or a proton as electrophile, followed by either proton abstraction or carbon dioxide loss from the resulting Wheland intermediate. This final study inverts this sequence by starting with the proton abstraction from an indolinone by a base to create/aromatize to a indole-2-enolate intermediate, which only then is followed by electrophilic attack (by iodine). Here I explore what light quantum chemical modelling might cast on the mechanism.
Read the rest of this entry »
Tags: Arenium ion, Bases, diazo, Diazonium compound, Electrophile, Electrophilic aromatic substitution, Equilibrium chemistry, Fortran, Indole, light quantum chemical modelling, Metal ions in aqueous solution, Nuclear physics, Simple aromatic rings, Solutions
Posted in Historical, reaction mechanism | No Comments »
January 5th, 2016
In May 2015, the EPSRC funding council in the UK required researchers to publish the outcomes of the funded work to include an OA (open access) version of the narrative and to cite the managed research data used to support the research with a DOI (digital object identifier). I was discussing these aspects with a senior manager (research outcomes) at the EPSRC and he asked me to provide some examples from my area of chemistry; here are some.
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted in Chemical IT | No Comments »
January 2nd, 2016
Another mechanistic study we started in 1972[cite]10.1039/P29770000281[/cite] is here 40+ years on subjected to quantum mechanical scrutiny.
Read the rest of this entry »
Tags: aqueous ethanoic acid solutions, energy, ethanoic acid solutions, free energy barrier , quantum chemical modelling
Posted in Historical, reaction mechanism | No Comments »
December 24th, 2015
The BBC TV quiz series Mastermind was first broadcast in the UK in 1972, the same time I was starting to investigate the mechanism of diazocoupling to substituted indoles as part of my Ph.D. researches. The BBC program became known for the catch phrase I've started so I'll finish; here I will try to follow this precept with the project I started then.  In 1972, one measured the rates of chemical reactions to gain insights into the transition state kinetic model. To obtain more data, we used isotopes such as 2H or 3H, together with substituents such as R-t-butyl to modify the potential energy surfaces of the reactions by inducing steric effects.[cite]10.1039/P29750001209[/cite],[cite]10.5281/zenodo.18777[/cite] We found that the kinetics for this reaction were actually complex‡ (in part because of pH dependence) involving a Wheland intermediate (the formation of which is shown with red curly arrows above) followed by the collapse of this intermediate to the diazo-coupled product (blue arrows). Coupling to 2-methyl indole (R=X=H, R'=Me), 2-t-butyl indole (R=H, R'=t-butyl) and 4-methyl-2-t-butyl indole (R=Me, R'=t-butyl) revealed that the kinetic isotope effects induced by replacing H by D or T were "not apparent" (i.e. close to 1), the inference being that the rate constant k1 for those systems was slower than k2; the formation of the Wheland intermediate was rate determining (the rds) for the reaction. But with 2-methyl-4,6-di-t-butyl indole (R=t-butyl, R'=Me) this changed and a deuterium isotope effect of ~7 was observed. The rate determining proton removal from the Wheland intermediate k2 was now slower than k1. With 2,4,6-tri-t-butyl indole, we ended by noting that the reaction become almost too slow to observe and furthermore was accompanied by loss of a t-butyl cation as well as a proton. At this point we attempted to infer some transition state models consistent with these observations. Note that we had relatively little data with which to derive our 3D models (one needs to define a geometry using 3N-6 variables, along with its relative energy and force constants). The text and diagram of our attempt is shown below.
In 1972, one measured the rates of chemical reactions to gain insights into the transition state kinetic model. To obtain more data, we used isotopes such as 2H or 3H, together with substituents such as R-t-butyl to modify the potential energy surfaces of the reactions by inducing steric effects.[cite]10.1039/P29750001209[/cite],[cite]10.5281/zenodo.18777[/cite] We found that the kinetics for this reaction were actually complex‡ (in part because of pH dependence) involving a Wheland intermediate (the formation of which is shown with red curly arrows above) followed by the collapse of this intermediate to the diazo-coupled product (blue arrows). Coupling to 2-methyl indole (R=X=H, R'=Me), 2-t-butyl indole (R=H, R'=t-butyl) and 4-methyl-2-t-butyl indole (R=Me, R'=t-butyl) revealed that the kinetic isotope effects induced by replacing H by D or T were "not apparent" (i.e. close to 1), the inference being that the rate constant k1 for those systems was slower than k2; the formation of the Wheland intermediate was rate determining (the rds) for the reaction. But with 2-methyl-4,6-di-t-butyl indole (R=t-butyl, R'=Me) this changed and a deuterium isotope effect of ~7 was observed. The rate determining proton removal from the Wheland intermediate k2 was now slower than k1. With 2,4,6-tri-t-butyl indole, we ended by noting that the reaction become almost too slow to observe and furthermore was accompanied by loss of a t-butyl cation as well as a proton. At this point we attempted to infer some transition state models consistent with these observations. Note that we had relatively little data with which to derive our 3D models (one needs to define a geometry using 3N-6 variables, along with its relative energy and force constants). The text and diagram of our attempt is shown below. 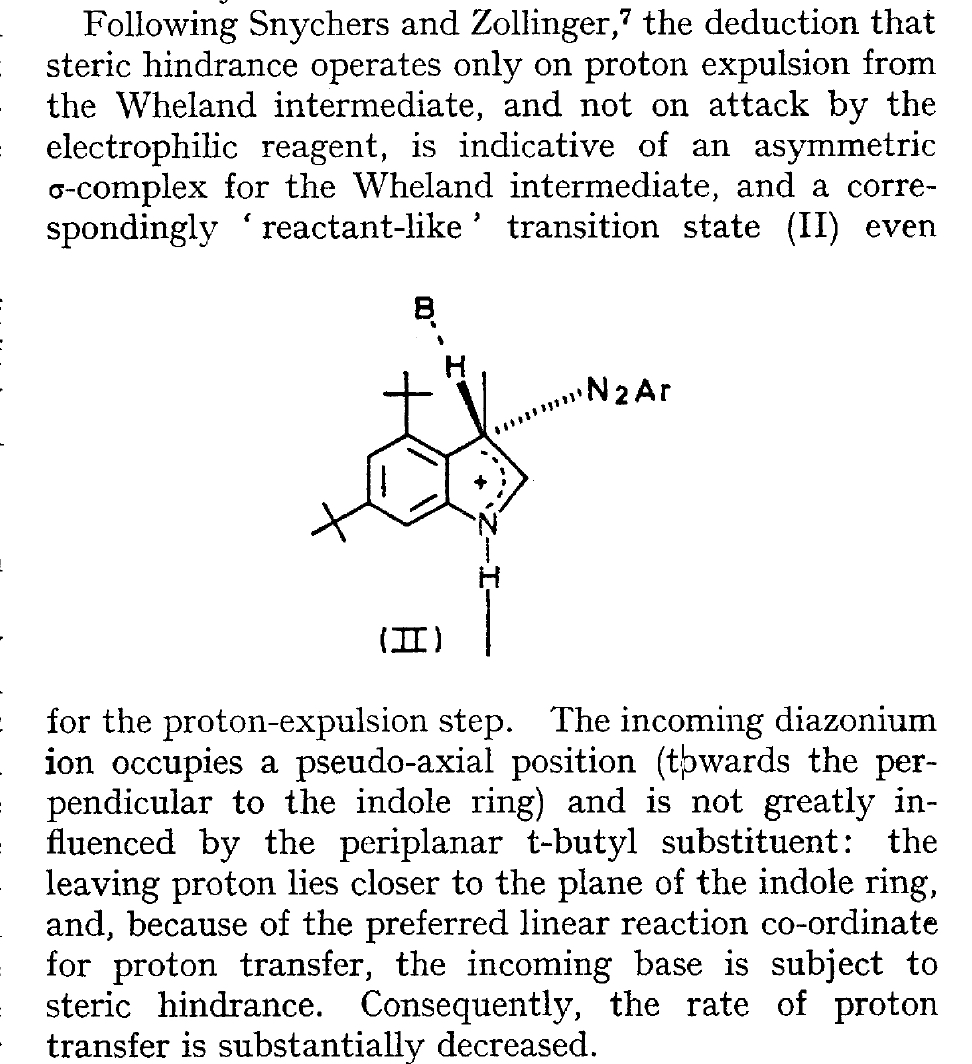 The main points of this argument were;
The main points of this argument were;
Read the rest of this entry »
Tags: Butyl, chemical reactions, Indole, Kinetic isotope effect, Organic chemistry, Physical organic chemistry, potential energy surfaces, relative energy
Posted in Historical, Interesting chemistry, reaction mechanism | 1 Comment »
December 20th, 2015
This question was posted on the CCL (computational chemistry list) by John McKelvey. Here, I give an answer in the form of a search of the CSD (crystal structure database).
Read the rest of this entry »
Tags: Azobenzene, John McKelvey, search azobenzene
Posted in Chemical IT, crystal_structure_mining | 5 Comments »
In 1972, one measured the rates of chemical reactions to gain insights into the transition state kinetic model. To obtain more data, we used isotopes such as 2H or 3H, together with substituents such as R-t-butyl to modify the potential energy surfaces of the reactions by inducing steric effects.[cite]10.1039/P29750001209[/cite],[cite]10.5281/zenodo.18777[/cite] We found that the kinetics for this reaction were actually complex‡ (in part because of pH dependence) involving a Wheland intermediate (the formation of which is shown with red curly arrows above) followed by the collapse of this intermediate to the diazo-coupled product (blue arrows). Coupling to 2-methyl indole (R=X=H, R'=Me), 2-t-butyl indole (R=H, R'=t-butyl) and 4-methyl-2-t-butyl indole (R=Me, R'=t-butyl) revealed that the kinetic isotope effects induced by replacing H by D or T were "not apparent" (i.e. close to 1), the inference being that the rate constant k1 for those systems was slower than k2; the formation of the Wheland intermediate was rate determining (the rds) for the reaction. But with 2-methyl-4,6-di-t-butyl indole (R=t-butyl, R'=Me) this changed and a deuterium isotope effect of ~7 was observed. The rate determining proton removal from the Wheland intermediate k2 was now slower than k1. With 2,4,6-tri-t-butyl indole, we ended by noting that the reaction become almost too slow to observe and furthermore was accompanied by loss of a t-butyl cation as well as a proton. At this point we attempted to infer some transition state models consistent with these observations. Note that we had relatively little data with which to derive our 3D models (one needs to define a geometry using 3N-6 variables, along with its relative energy and force constants). The text and diagram of our attempt is shown below.
 The main points of this argument were;
The main points of this argument were;