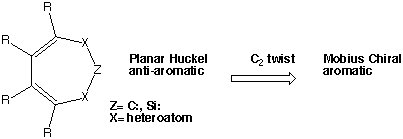

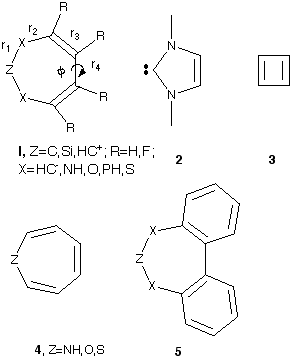
| Table 1. Ab initio calculated properties for 1 and 5. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Energy, Hartree (B3LYP/6-31G*) | NICS, ppm | r1,r2,r3,r4,f | Point Group Symmetry |
| Z=C:, X=NH, R=H | -303.5375a | 21.1 | 1.360,1.428,1.337,1.468, 14.3 | C2 |
| Z=C:, X=NH, R=H | -303.6241b | 23.6 | 1.352,1.425,1.331,1.467, 0.0 | C2vc |
| Z=C:, X=NH, R=H | -303.6243b | 19.4 | 1.354,1.425,1.331,1.465, 18.4 | C2 |
| Z=C:, X=NH, R=H, triplet | -303.5792b | -8.3 | 1.375,1.370,1.417,1.373, 0.0 | C2v |
| Z=C:, X=NH, R=F | -700.4496 | 1.2 | 1.367,1.410,1.366,1.450,33.189 | C2 |
| 5, X=NH | -610.8548 | 8.9 | 1.360,1.426,1.409,1.487, 35.7 | C2 |
| Z=C:, X=O, R=H | -343.3315b | 15.2 | 1.333,1.407,1.325,1.456, 0.0 | C2vd |
| Z=C:, X=O, R=H | -343.3340b | 7.7 | 1.332,1.405,1.326,1.452, 24.9 | C2 |
| Z=C:, X=O R=H | -343.2339e | 8.8 | 1.345,1.405,1.333,1.456, 23.7 | C2 |
| Z=C:, X=O, R=F | -740.1387 | -1.3 | 1.353,1.379,1.334,1.448, 29.0 | C2 |
| 5, X=O | -650.5536 | 6.3 | 1.343,1.410,1.400,1.474, 32.2 | C2 |
| Z=C:, X=HC-, R=H | -270.0042 | 77.7 | 1.362 (1.530), 1.531 (1.380), 1.366 (1.436), 1.445, 0.0 | Csf |
| Z=C:, X=HC-, R=H | -270.0083 | 24.7 | 1.354 (1.506), 1.526 (1.372), 1.391 (1.464), 1.423, 18.8 | C1 |
| Z=C:, X=HC-, R=F | -865.5182 | -3.5 | 1.337 (1.430), 1.459 (1.362), 1.353 (1.424), 1.402, 25.5 | C1 |
| Z=CH+, X=NH, R=H | -303.9659 | 21.0 | 1.321,1.445,1.331,1.474, 21.4 | C2 |
| Z=CH+, X=O, R=H | -343.6329 | 14.6 | 1.273,1.447,1.325,1.468, 15.4 | C2 |
| Z=CH+, X=HC-, R=H | -270.8684 | 79.4 | 1.404 (1.393), 1.452 (1.465), 1.356 (1.350), 1.500, 25.4 | C1 |
| Z=CH+, X=HC-, R=F | -965.5308 | -7.5 | 1.384, 1.421, 1.347, 1.450, 48.4 | C2 |
| Z=C:, X=PH, R=H | -876.6275 | 41.3 | 1.673,1.660,1.480,1.340, 0.0 | Cs |
| Z=C:, X=PH, R=H | -876.6920 | 7.1 | 1.707,1.830,1.348,1.469,35.7 | C2 |
| Z=C:, X=S, R=H | -989.1832 | 18.4 | 1.654,1.820,1.340,1.470, 0.0 | C2v |
| Z=C:, X=S, R=F | -1386.0821 | 2.3 | 1.654,1.826,1.3381.459,38.4 | C2 |
| Z=Si:, X=NH, R=H | -555.01480 | 14.0 | 1.748,1.414,1.344,1.464,23.69 | C2 |
| Z=Si:, X=O, R=H | -594.77315 | 7.4 | 1.678,1.375,1.341,1.462,22.9 | C2 |
| Z=Si:, X=PH, R=H | -1128.1269 | 29.5 | 2.183, 1.807, 1.348, 1.474, 0.0 | C2vg |
| Z=Si:, X=PH, R=H | -1128.1596 | 4.7 | 2.256,1.828,1.348,1.465, 46.9 | C2 |
| Z=Si:, X=PH, R=H | -1128.0819 | 25.5 | 2.254,1.670,1.470,1.340, 0.0 | Cs |
| Z=Si:, X=S, R=H | -1240.6793 | 5.2 | 2.178,1.790,1.330,1.460, 50.0 | C2 |
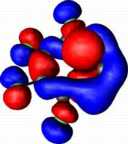
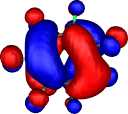
| HOMO-3 for Z=C:, X=O, R=F |
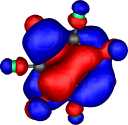
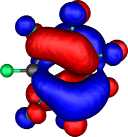
HOMO for Z=CH+, X=HC-, R=F |
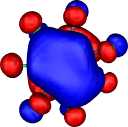
HOMO-1 | HOMO-2 | HOMO-3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |